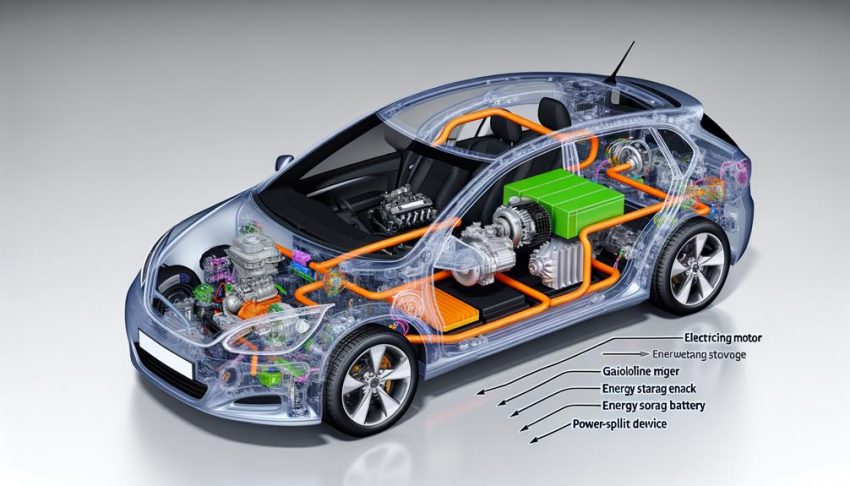
When you think about how a Prius hybrid car works, it's fascinating to see the synergy between its gasoline engine and electric motor. This vehicle operates on a series-parallel design, which means at low speeds, it can run solely on electric power, offering zero emissions. But what happens when you need more power or start braking? That's where the gasoline engine and regenerative braking system kick in, capturing kinetic energy and converting it to electricity for battery storage. Curious about the intricate mechanics behind this and the common issues hybrid users face? Let's explore further.
Contents
Prius Design
The aerodynamic design of the Prius plays a critical role in its efficiency. By reducing drag, the Toyota Prius achieves better fuel economy, a hallmark of its hybrid system. Particularly in the Gen 3 model, the vehicle's longer and wider body optimizes airflow, lowering the drag coefficient from 0.26 to an impressive 0.25. This aerodynamic refinement translates directly to enhanced speed efficiency and reduced fuel consumption.
You'll find that the Gen 3 Prius doesn't just rely on its shape for efficiency gains. The vehicle's fuel economy saw an improvement from 48 to 51 MPG, thanks to a combination of aerodynamic advances and a lighter transmission design. These design choices work in tandem, allowing the hybrid system to operate more effectively, conserving energy and reducing emissions.
Furthermore, the Gen 3 Prius features an upgraded engine, moving from 76 horsepower (1.5 L) to 98 horsepower (1.8 L). This enhancement provides better acceleration and overall performance without compromising the vehicle's renowned fuel efficiency. The integration of this more powerful engine with the Prius's aerodynamic design guarantees that you enjoy a smoother, more responsive driving experience.
Your experience as a driver is further augmented by the multi-function display, which monitors critical aspects like energy flow, battery levels, and braking systems. This display doesn't just offer information—it actively enhances your awareness of the vehicle's efficiency, allowing you to make informed driving decisions that maximize the benefits of the hybrid system.
Hybrid Engine Mechanics
In understanding the hybrid engine mechanics of the Prius, you'll find it employs a series-parallel design that allows the electric motor and gasoline engine to operate independently or together. The power split device guarantees seamless shifts between these power sources, optimizing performance based on driving conditions. This system, combined with regenerative braking and a sophisticated power control unit, maximizes fuel efficiency and minimizes emissions.
Series-Parallel Hybrid Design
Harnessing both a gasoline engine and an electric motor, the series-parallel hybrid design in a Prius optimizes fuel efficiency and performance through a sophisticated power distribution system. Unlike a pure series hybrid, where the electric motor is the sole propulsion source, the Prius combines the strengths of both power sources. At low speeds or during initial acceleration, the electric motor is the primary driver, benefiting from an uninterrupted power supply generated internally, eliminating the need for external recharging.
The power split device is a critical component of the Prius's hybrid system. It connects the generator, gasoline engine, and electric motor, ensuring seamless shifts between power sources. When higher power is required, the gasoline engine kicks in, either working in tandem with or independently from the electric motor. This versatility allows the Prius to achieve impressive fuel efficiency, with models ranging from 52 to 56 MPG.
Optimal Power Distribution
Achieving ideal power distribution in a Prius hybrid requires an intricate balance between the gasoline engine and the electric motor. The vehicle employs a series-parallel hybrid design to guarantee peak power distribution based on driving conditions. A power split device integrates the gas engine, generator, and electric motor, enabling seamless shifts between power sources to maximize both efficiency and performance.
At low speeds, the electric motor primarily powers the vehicle, drawing energy from the hybrid battery. This setup enhances fuel savings, especially in urban driving scenarios where frequent stops are typical. When you accelerate, the gasoline engine and electric motor combine their outputs, utilizing additional energy from the hybrid battery to provide a smooth and responsive driving experience.
The regenerative braking system plays a key role in maintaining energy efficiency. During deceleration, it captures kinetic energy and converts it back into electricity, which is then stored in the hybrid battery. This process not only improves overall energy efficiency but also reduces wear on the conventional braking system. By meticulously balancing these elements, the Prius guarantees that you're always operating under peak power distribution conditions, whether you're driving in the city or accelerating on the highway.
Starting From a Stop
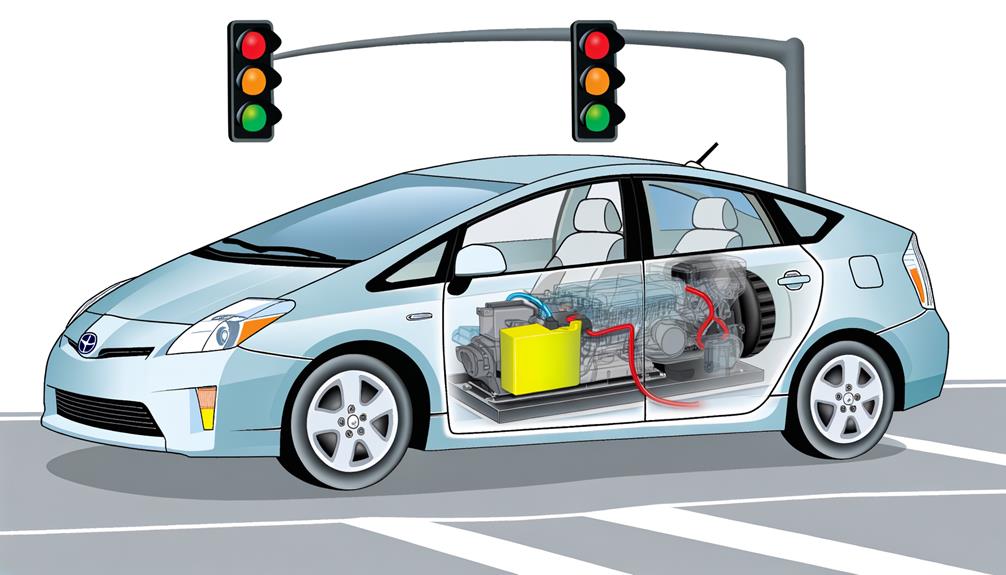
When you start from a stop in a Prius, the electric motor powers the vehicle using energy from the hybrid battery, resulting in zero emissions at low speeds. As you accelerate past 15 MPH, the gasoline engine engages seamlessly to provide additional power. This efficient shift between electric and gasoline propulsion is managed by the power control unit, optimizing fuel efficiency in urban driving conditions.
Electric Motor Activation
Upon pressing the accelerator from a complete stop, the Toyota Prius relies on its electric motor for initial propulsion, drawing energy from the onboard battery. This hybrid car design guarantees that the electric motor provides the necessary torque to move the vehicle efficiently at low speeds, particularly effective in urban environments characterized by frequent stop-and-start traffic. By utilizing the electric motor in these conditions, the Prius minimizes fuel consumption and offers substantial fuel economy benefits compared to traditional gasoline engines.
The electric motor's activation at low speeds not only conserves fuel but also delivers a smooth and quiet driving experience. This design maximizes efficiency and reduces emissions during city driving where the vehicle often operates below 15 MPH. The shift from the electric motor to the gasoline engine is seamless, assuring that you experience uninterrupted power delivery as you accelerate.
At speeds exceeding 15 MPH, the gasoline engine starts to assist, but during initial acceleration, the electric motor's contribution is pivotal. This system optimizes the hybrid car's overall performance, allowing for sophisticated energy management and considerable fuel savings, making the Toyota Prius an exemplary model of hybrid technology.
Gas Engine Engagement
After the Prius reaches approximately 15 MPH, the gasoline engine seamlessly engages, supplementing the electric motor's efforts. This change is essential for maintaining ideal power to the wheels, especially as the vehicle demands more energy at higher speeds. The hybrid system is designed to harness the strengths of both the gas engine and electric motor, ensuring that the vehicle operates efficiently under varying driving conditions.
When starting from a complete stop, the Prius relies solely on its electric motor, utilizing battery energy to propel the vehicle. This method is particularly effective for city driving and stop-and-start traffic, greatly enhancing fuel efficiency and reducing emissions. As speed increases, the gas engine automatically engages, providing additional power necessary for acceleration and sustained driving. This dual-engagement system allows the Prius to achieve a balance between performance and fuel savings.
The shift from electric to gasoline power is meticulously engineered to be smooth and unobtrusive, contributing to overall driving comfort. By minimizing fuel consumption and emissions at low speeds, the Prius offers an environmentally friendly solution for urban driving. This sophisticated interaction between the gas engine and electric motor exemplifies Toyota's commitment to both efficiency and performance.
Braking and Energy Recovery
Regenerative braking embodies the innovative spirit of the Prius, capturing approximately 70% of kinetic energy normally lost during deceleration. This energy recovery process is essential in optimizing the vehicle's efficiency. As you decelerate, the regenerative braking system converts kinetic energy into electrical energy, which is then stored in the hybrid battery. This not only extends the driving range but also greatly enhances fuel efficiency by utilizing this stored energy for future low-speed driving, particularly beneficial in urban traffic conditions.
When the Prius comes to a complete stop, both the internal combustion engine and the electric motor shut off. This action is meticulously designed to conserve battery power while maintaining essential functions such as the radio and lights. During this phase, the hybrid battery plays a vital role in supporting these auxiliary systems, ensuring the vehicle remains operational without unnecessary fuel consumption.
The advantages of regenerative braking extend beyond energy recovery. By reducing reliance on traditional friction brakes, the system minimizes brake wear, contributing to a smoother driving experience and lowering maintenance costs. This continuous recycling of kinetic energy not only boosts the Prius's fuel economy but also positively impacts its environmental footprint by reducing emissions.
Common Hybrid Issues

While hybrid vehicles like the Prius offer numerous benefits, they aren't without their challenges. One of the primary concerns is the hybrid battery. Over time, the battery can degrade, leading to diminished performance and, eventually, the need for costly repairs or replacements. Although hybrid batteries come with an eight-year or 100,000-mile warranty, some may require attention earlier due to faulty cells.
Maintenance of a hybrid vehicle can be more complex compared to traditional cars. The intricate design of systems integrating the hybrid battery and the internal combustion engine often complicates repair processes. This complexity can lead to higher labor costs and longer service times, as specialized knowledge and tools are typically necessary.
If the hybrid battery fails, the Prius will rely solely on its internal combustion engine. This shift not only reduces the vehicle's fuel efficiency but also increases fuel costs, negating one of the primary advantages of owning a hybrid. It's vital to monitor the health of the hybrid battery and address any issues promptly to prevent such scenarios.
When it comes to replacing a hybrid battery, you have options. Dealership batteries are generally more reliable but come with a higher price tag. Alternatively, cost-effective aftermarket solutions are available, though their quality can vary greatly. Choosing the right replacement option is essential for maintaining the performance and longevity of your Prius.
Environmental Benefits
Hybrid vehicles like the Toyota Prius offer substantial environmental benefits that greatly outperform traditional gasoline-powered cars. With markedly higher fuel efficiency, Prius models achieve between 52 to 56 MPG, compared to the average vehicle's 39.4 MPG. This enhanced fuel efficiency translates to lower fuel consumption and emissions, which is essential for reducing your carbon footprint.
The Prius operates with zero emissions during electric-only driving, a feature particularly beneficial in urban settings with frequent stop-and-go traffic. This capability guarantees a reduction in harmful pollutants, contributing to cleaner air in densely populated areas. Additionally, the car maximizes energy efficiency through regenerative braking, converting approximately 70% of the kinetic energy lost during deceleration back into usable energy. This reduction in energy waste means you're burning less fuel to power the vehicle.
Furthermore, the combination of a gasoline engine and electric motor in the Prius results in lower overall carbon footprints, a critical factor in combating climate change. The reduced emissions not only contribute to a healthier planet but also align with sustainability goals by minimizing dependence on fossil fuels. This makes the Toyota Prius an ideal choice for environmentally conscious consumers.
- Fuel Efficiency: Achieves 52-56 MPG compared to 39.4 MPG average.
- Zero Emissions: Zero emissions during electric-only driving, especially useful in urban areas.
- Regenerative Braking: Recovers about 70% of kinetic energy during deceleration.
- Lower Carbon Footprints: Combines gasoline and electric power to reduce emissions.
Frequently Asked Questions
At What Speed Does the Prius Switch to Gas?
The Prius typically switches to the gasoline engine at speeds exceeding 15 MPH. The electric motor handles lower speeds and stop-and-go traffic, enhancing fuel efficiency. Regenerative braking also contributes to ideal energy usage and overall efficiency.
How Does the Prius Hybrid System Work?
You'll find the Prius hybrid system optimizes fuel efficiency by using an electric motor for low speeds and regenerative braking to recharge the battery. The gasoline engine aids at higher speeds, ensuring a seamless and efficient driving experience.
Does a Prius Hybrid Charge While Driving?
Yes, a Prius hybrid charges while driving. Its regenerative braking system captures kinetic energy, and its electric motor works with the gasoline engine. The battery management system optimizes energy flow, ensuring constant recharging during your drive.
How Long Does a Hybrid Battery Last in a Prius?
Considering the battery lifespan of 8-15 years in a Prius, replacement costs can vary widely. For best longevity, follow maintenance tips like regular check-ups and longer drives to avoid depletion and guarantee sustainable performance.
Conclusion
To summarize, you've seen how the Prius' series-parallel design optimizes fuel efficiency by seamlessly integrating a gasoline engine and an electric motor. Starting from a stop, the electric motor propels the vehicle, while regenerative braking recaptures energy during deceleration. While common hybrid issues may arise, the environmental benefits are substantial, offering reduced emissions and impressive fuel economy. Understanding these mechanics provides a clear picture of the Prius' innovative approach to sustainable driving.